Aug 31, 2020 SpaceX launches first polar orbit mission from Cape Canaveral since 1969 The rideshare payload separations wrapped up the first launch into polar orbit from Florida's Space Coast in more than 50. The polar satellites revolve around the Earth in a north-south orbit passing over the poles as the Earth spins about its north-south axis. It is a satellite whose orbit is perpendicular or at right angles to the equator, or in simple words it passes over the north and south poles as it orbits the earth. Jun 07, 1996 Polar orbiting satellites are an important class of meteorological and geophysical satellite. Guitar pro 7 no sound bar. Typically, these satellites are placed in circular sun-synchronous orbits. Their altitudes usually range from 700 to 800 km, with orbital periods of 98 to 102 minutes. Polar orbit A satellite orbit in which the satellite passes over the North and South poles on each orbit, and eventually passes over all points on the earth. The angle of inclination between the equator and a polar orbit is 90 degrees. Dictionary of Military and Associated Terms.
Three Classes of Orbit
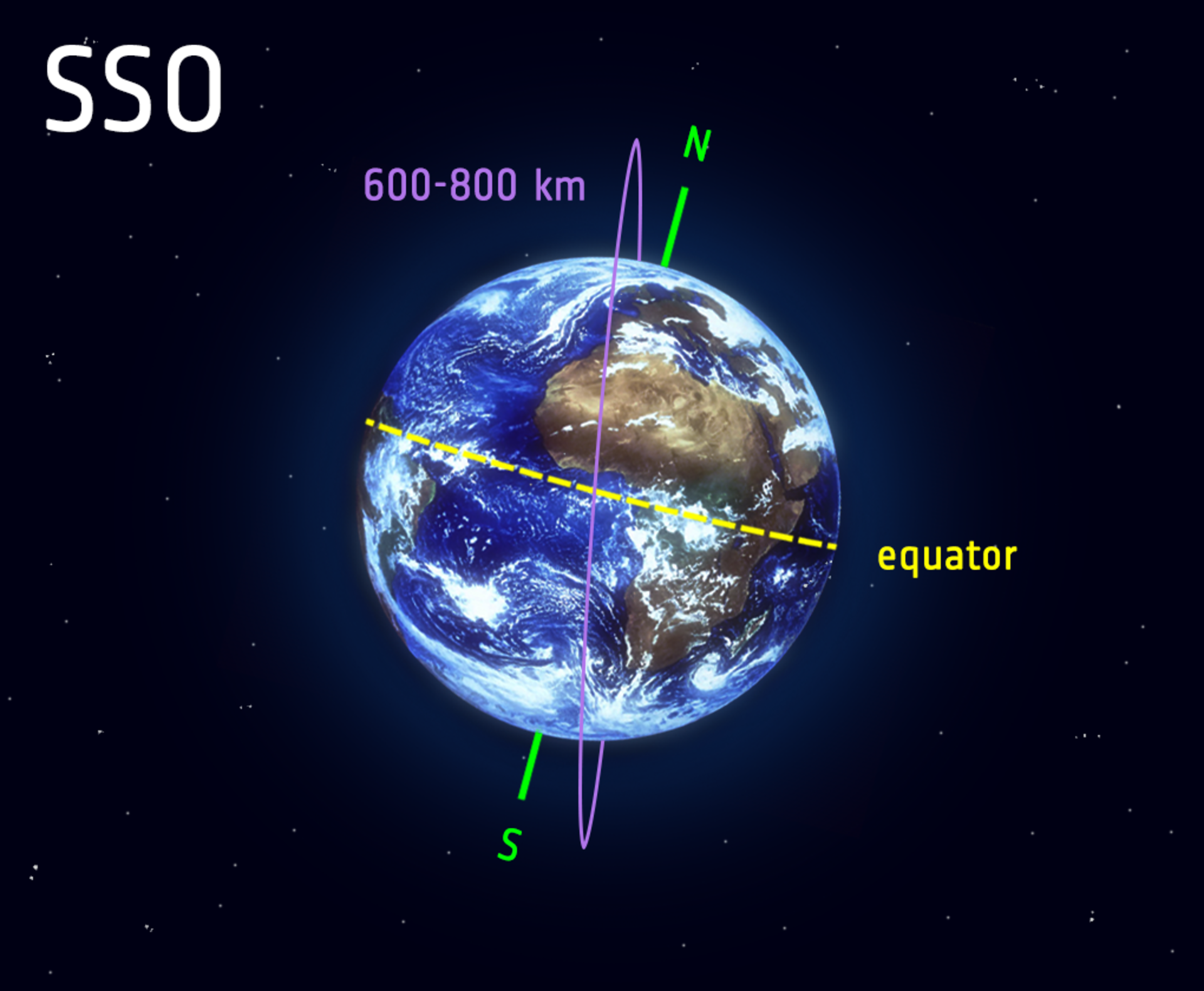
Near Polar Orbit
High Earth Orbit
Polar Orbit Launch
When a satellite reaches exactly 42,164 kilometers from the center of the Earth (about 36,000 kilometers from Earth's surface), it enters a sort of 'sweet spot' in which its orbit matches Earth's rotation. Capture one 20 nikon. Because the satellite orbits at the same speed that the Earth is turning, the satellite seems to stay in place over a single longitude, though it may drift north to south. This special, high Earth orbit is called geosynchronous.
A satellite in a circular geosynchronous orbit directly over the equator (eccentricity and inclination at zero) will have a geostationary orbit that does not move at all relative to the ground. It is always directly over the same place on the Earth's surface.
A geostationary orbit is extremely valuable for weather monitoring because satellites in this orbit provide a constant view of the same surface area. When you log into your favorite weather web site and look at the satellite view of your hometown, the image you are seeing comes from a satellite in geostationary orbit. Every few minutes, geostationary satellites like the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) satellites send information about clouds, water vapor, and wind, and this near-constant stream of information serves as the basis for most weather monitoring and forecasting.
If I run SHOW DATABASES command the database shows up and I can use/see the tables with the commands. Restarting DBeaver resolves the issue, edit in that the ones created before the restart show up but ones after the restart have same problem.

